November 2025: RSV Prefusion F Vaccine for Prevention of Hospitalization in Older Adults
A large, real-world randomized trial in Denmark found that the single-dose RSVpreF vaccine substantially reduced hospitalizations for RSV in adults aged 60 and older during the 2024–2025 season, with similar rates of serious adverse events to no vaccine.

October 2025: A Randomized Trial of Physical Therapy for Meniscal Tear and Knee Pain
For adults 45–85 with knee pain, osteoarthritis, and a degenerative meniscal tear, adding clinic-based physical therapy or motivational text messages did not reduce pain more than a well-structured home-exercise program alone over 3 months. Pain and function improved substantially in all groups.

September 2025: A Randomized Trial of Shunting forIdiopathic Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus
In older adults with idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH), a double-blind randomized trial showed that turning a programmable shunt “on” significantly improved walking speed and balance at 3 months versus a placebo (near-closed) setting, while cognition and bladder symptoms did not measurably improve. Falls were less common with an open shunt, but subdural bleeds and positional headaches were more frequent and require monitoring.

August 2025: Reduction of Antihypertensive Treatment in Nursing Home Residents
Reduction of Antihypertensive Treatment in Nursing Home Residents

July 2025: Self-Neglect in Older People — Clinical, Social & Ethical Challenges
Self-neglect is the most common reason for maltreatment of the elderly.
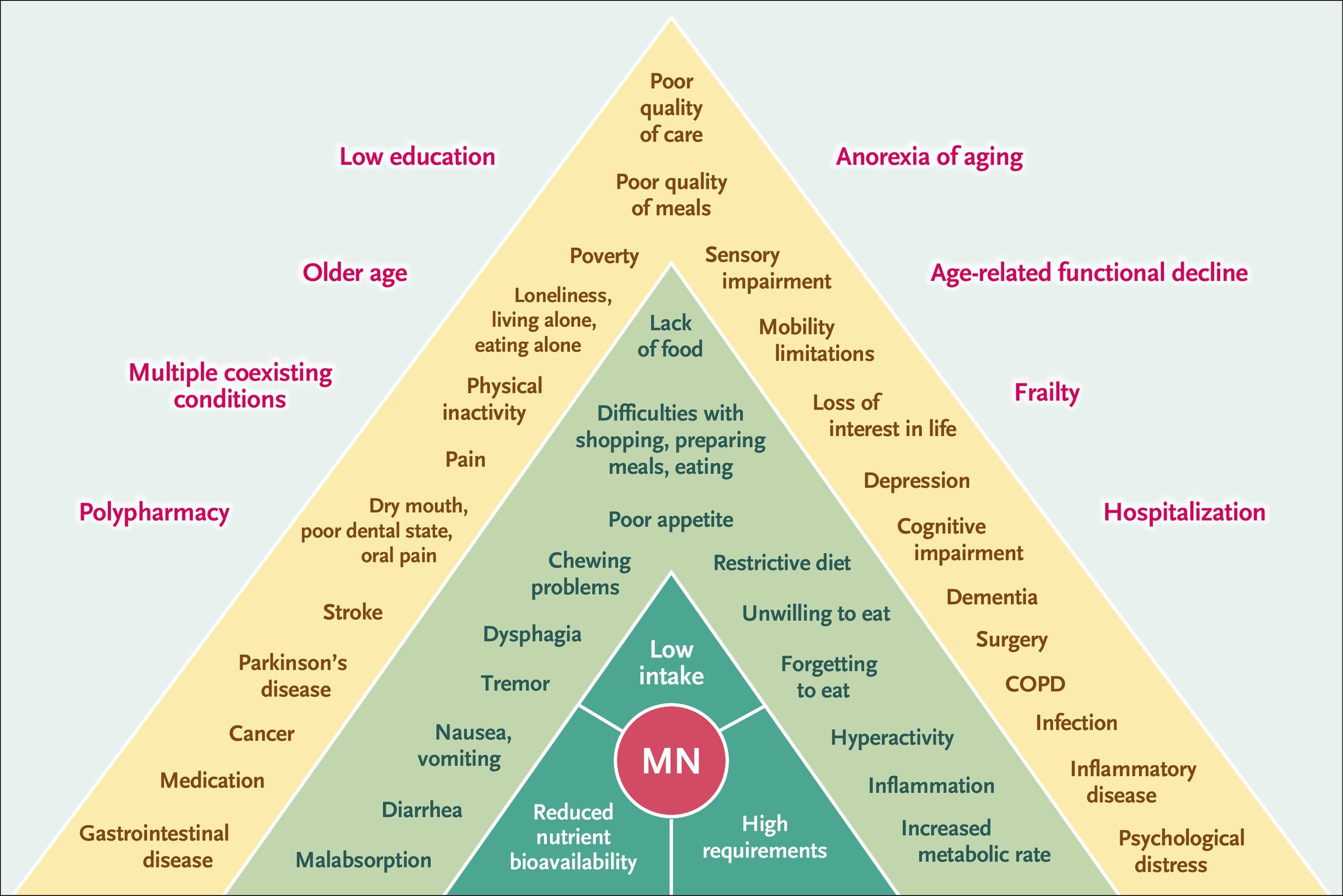
June 2025: Malnutrition in Older Adults
Malnutrition (undernutrition) is widespread among older adults and leads to disability, longer hospital stays, poorer recovery, lower quality of life, and higher medical costs.
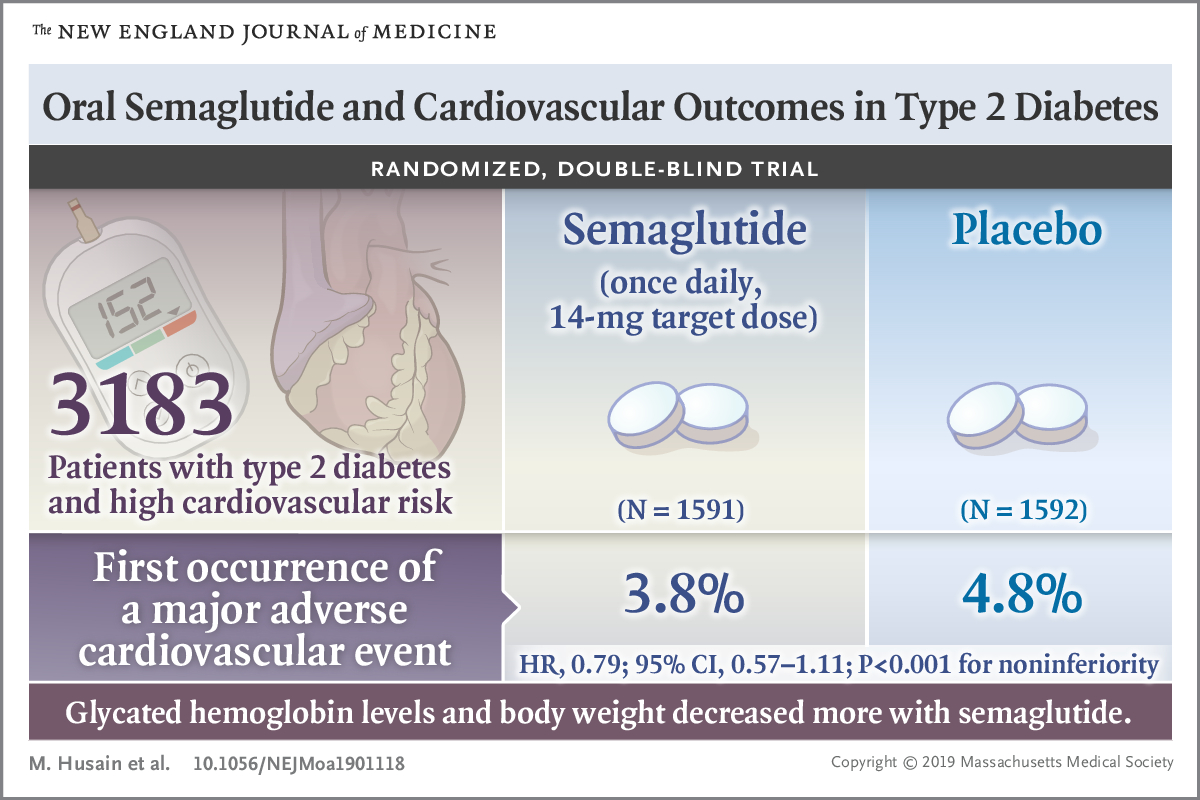
May 2025: Oral Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in High-Risk Type 2 Diabetes
Heart attacks and strokes remain the leading killers of people with type 2 diabetes. A large international trial found that the once‑daily tablet oral semaglutide cut those events by 14 percent versus placebo in high‑risk adults.
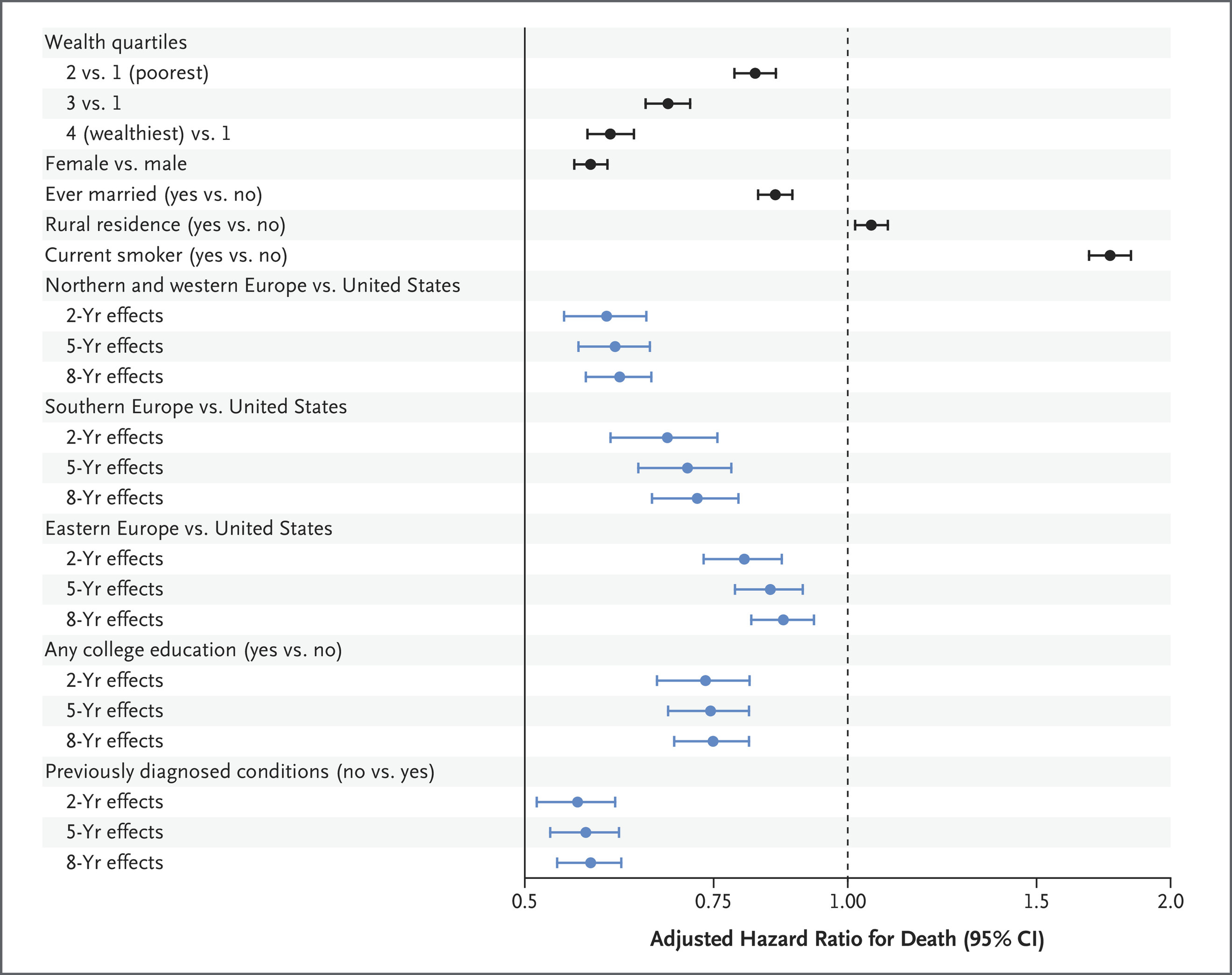
April 2025: Association between Wealth and Mortality in the United States and Europe
Low wealth shortens life: the poorer an older adult is, the higher their risk of dying—and the rich–poor survival gap is wider in the United States than anywhere in Europe.
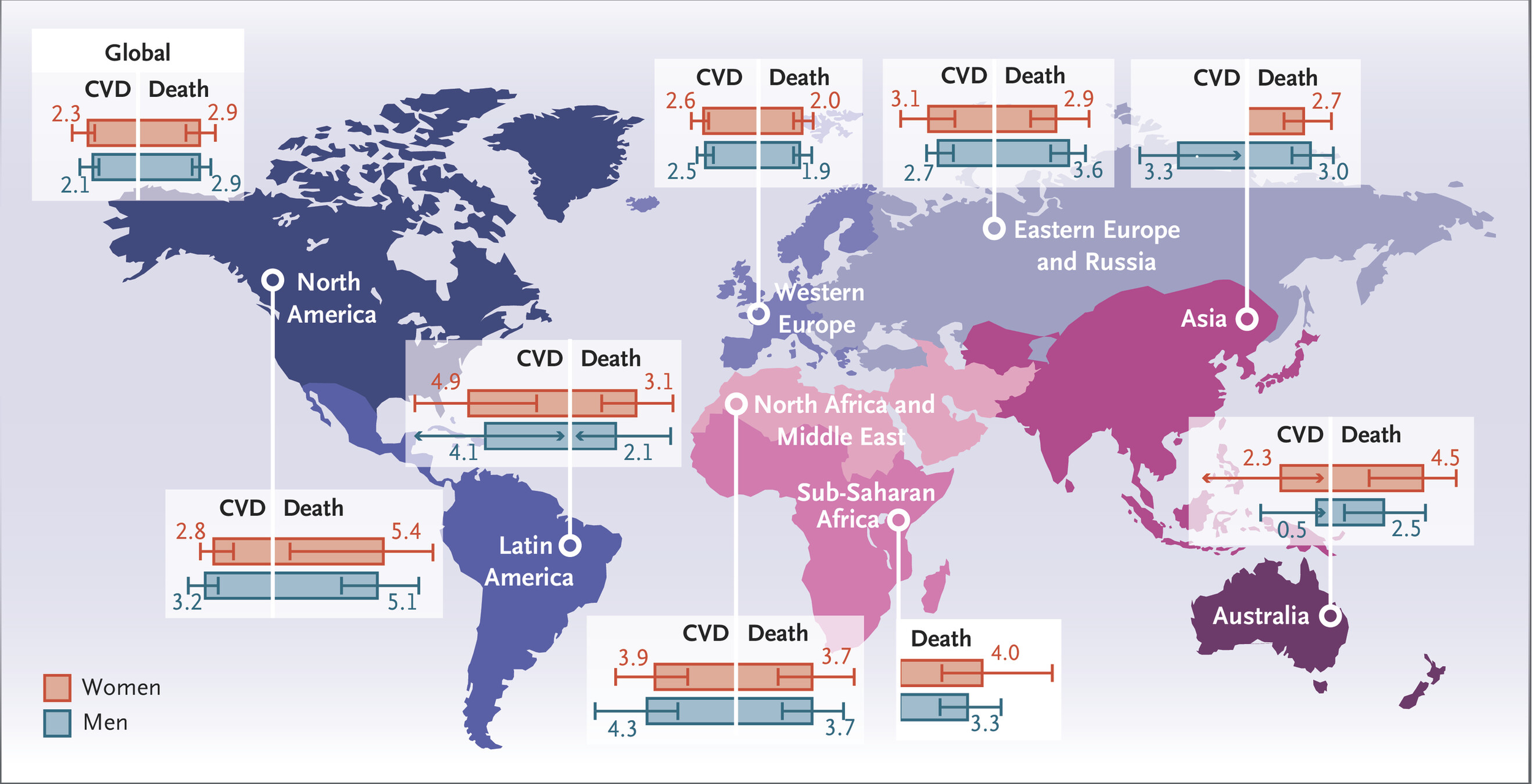
March 2025: Global Effect of Cardiovascular Risk Factors on Lifetime Estimates
Five common, modifiable factors — high blood pressure, high “bad” cholesterol, unhealthy weight (either too low or too high), diabetes, and smoking — account for roughly half of all cardiovascular disease worldwide. When all five are present at age 50, lifetime risk of heart attack or stroke jumps to 24 % in women and 38 % in men.
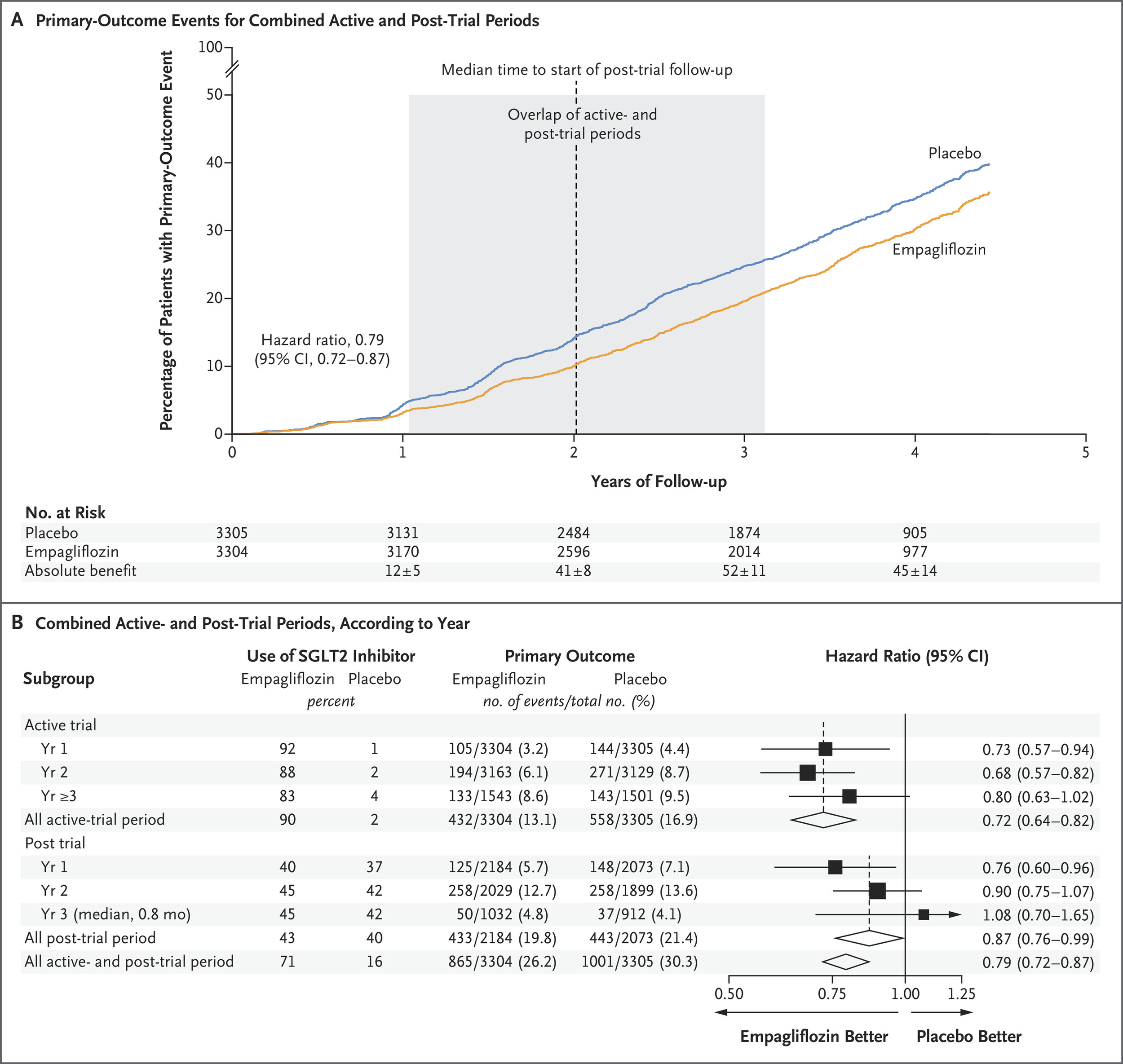
February 2025: Long-Term Effects of Empagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease
A two‑year course of the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin continued to protect kidneys and hearts for up to a year after the drug was stopped, cutting the combined risk of kidney progression or cardiovascular death by about 20 %.
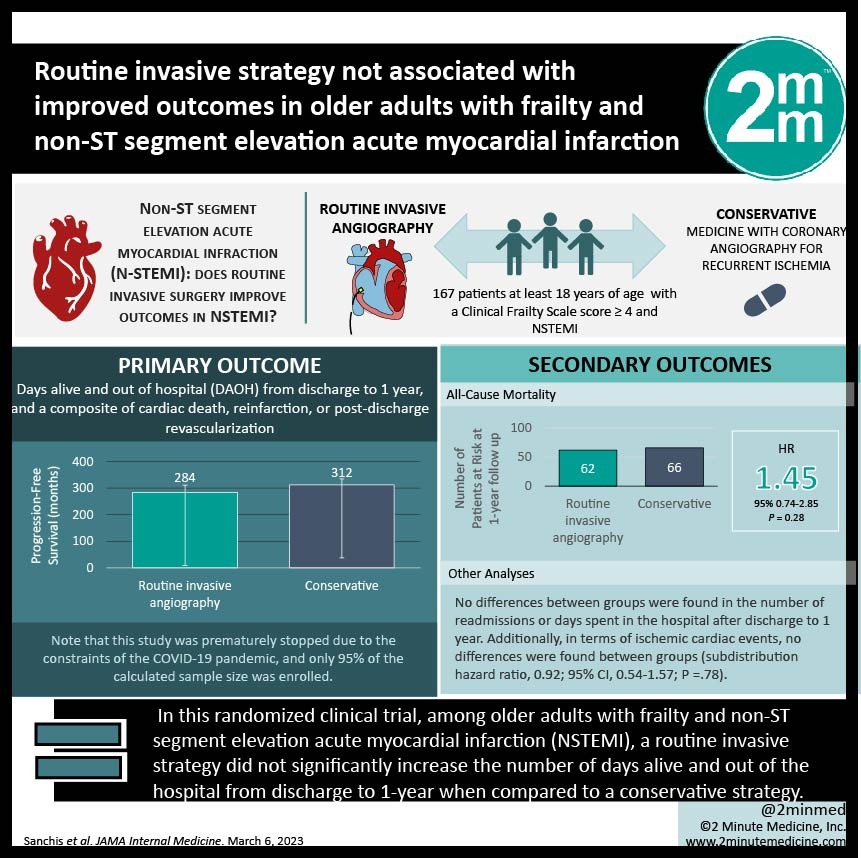
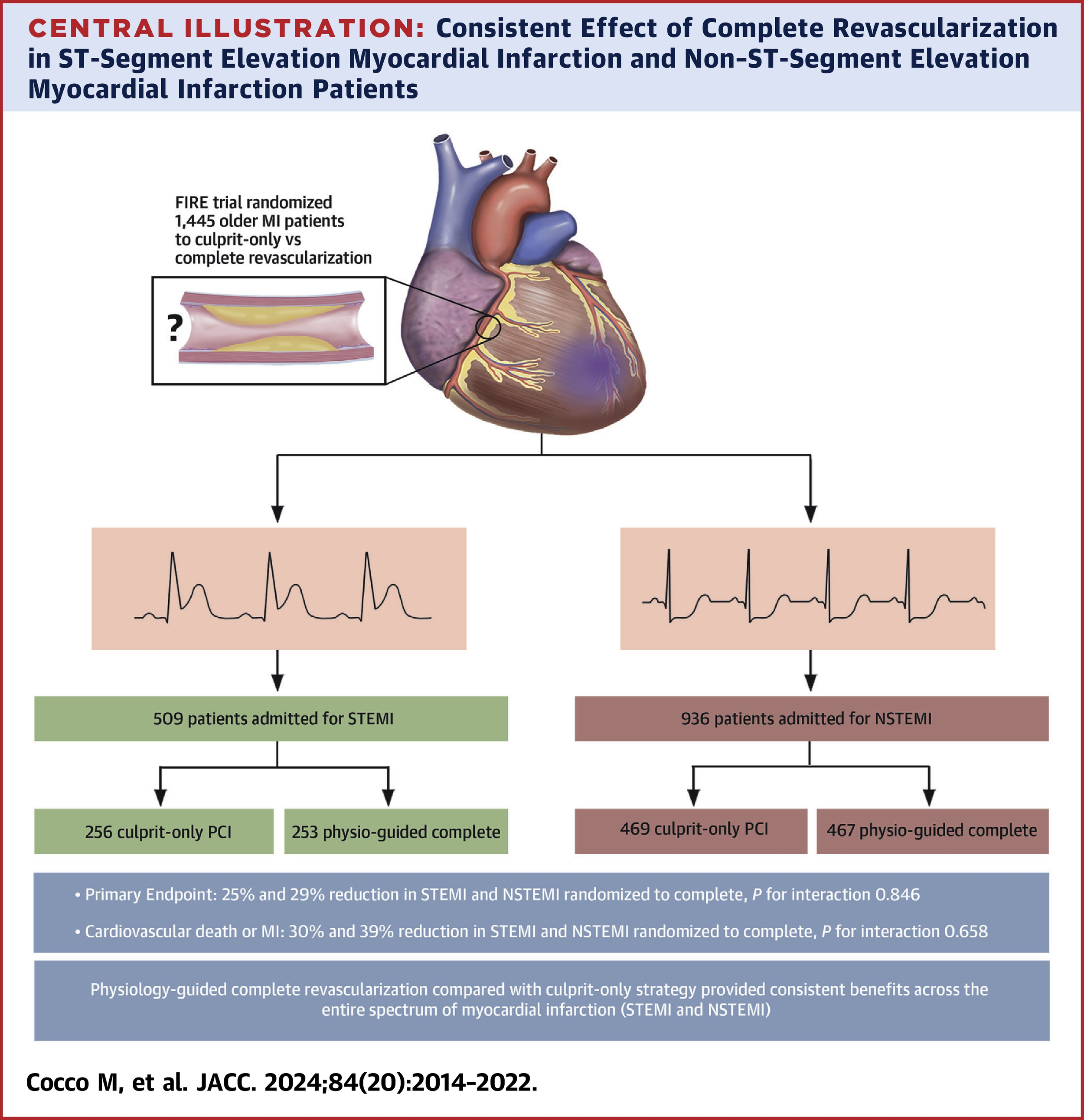
January 2025: Invasive Strategy for Older Patients with MI
A major trial in adults ≥ 75 with non‑ST‑segment–elevation heart attacks (NSTEMI) found that routinely sending everyone for angiography and possible stent surgery did not lower the death rate compared with careful medical therapy alone.
What do I need to know?
In the SENIOR‑RITA study, only half of the patients assigned to the “invasive” arm actually received a stent, partly because the average wait for the procedure was five days. Still, the invasive strategy did cut non‑fatal heart‑attack recurrences but offered no survival edge. Decisions were highly individualized: doctors weighed bleeding risk, frailty, cognition, life expectancy, and patient preferences before choosing invasive or conservative care. Current guidelines now rate early (within 24 h) angiography in older NSTEMI patients as optional rather than essential because pooled data show no clear mortality benefit.

December 2024: Long-Term Oxygen Therapy for 24 or 15 Hours per Day
A recent trial in patients with severe resting hypoxemia showed that prescribing long‑term oxygen therapy (LTOT) for 24 hours a day did not reduce the combined risk of hospitalization or death within one year compared with 15 hours a day.

November 2024: Simple Strategies to Reduce Cardiac Strain in Older Adults in Extreme Heat
Extreme heat places older adults — especially those with heart disease — at high risk of dangerous spikes in heart rate and blood pressure. Simple cooling tactics such as electric fans and skin wetting have been debated, but their true benefits and harms were unclear.
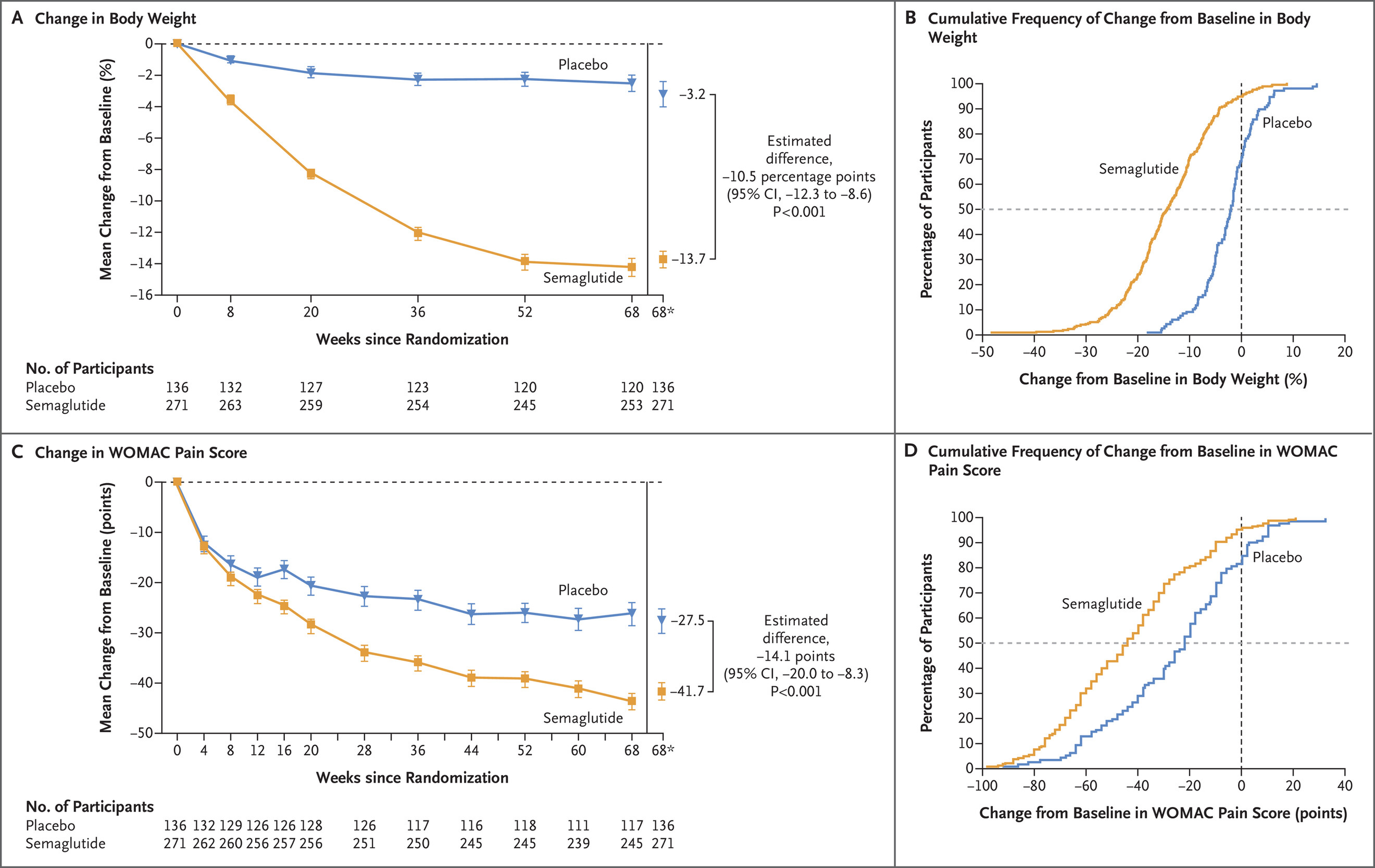
October 2024: Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Persons with Obesity and Knee Osteoarthritis
Weekly injections of the weight‑loss drug semaglutide 2.4 mg relieved knee‑osteoarthritis pain far better than placebo while trimming body weight, with no extra serious side‑effects.
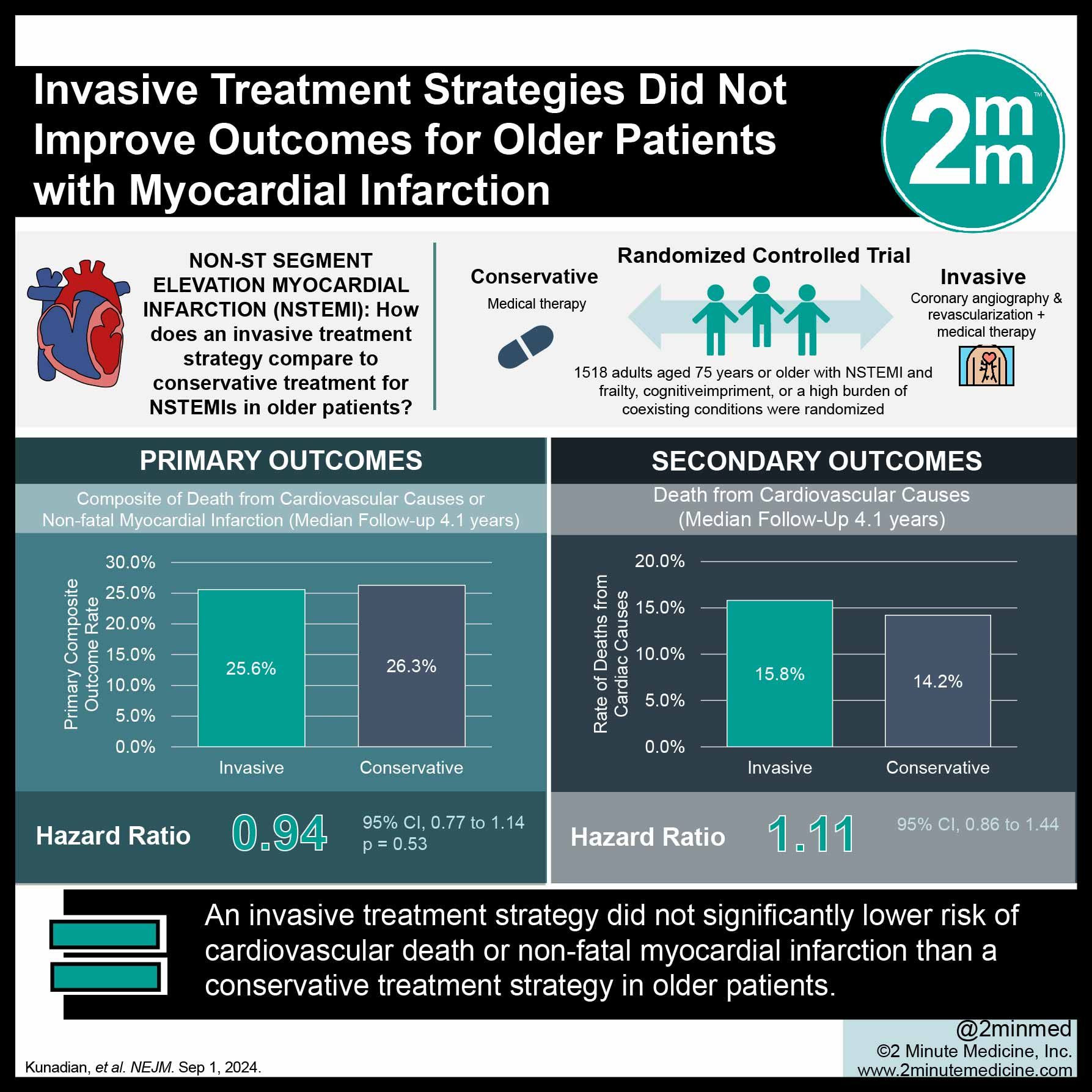
September 2024: Invasive Treatment Strategy for Older Patients with Myocardial Infarction
For adults ≥ 75 admitted with non‑ST‑segment‑elevation heart attack (NSTEMI), routinely taking everyone to the cath‑lab for angiography and possible stent placement did not improve survival compared with optimized drug therapy alone in the 1,518‑patient SENIOR‑RITA trial.

August 2024: Frailty in Older Adults
Frailty is a state of reduced physiologic reserve that becomes steadily more common with age: worldwide surveys show its prevalence climbs from ≈11 % in people aged 50–59 to over 50 % in those ≥ 90, especially among hospital or nursing‑home residents and the socially vulnerable.
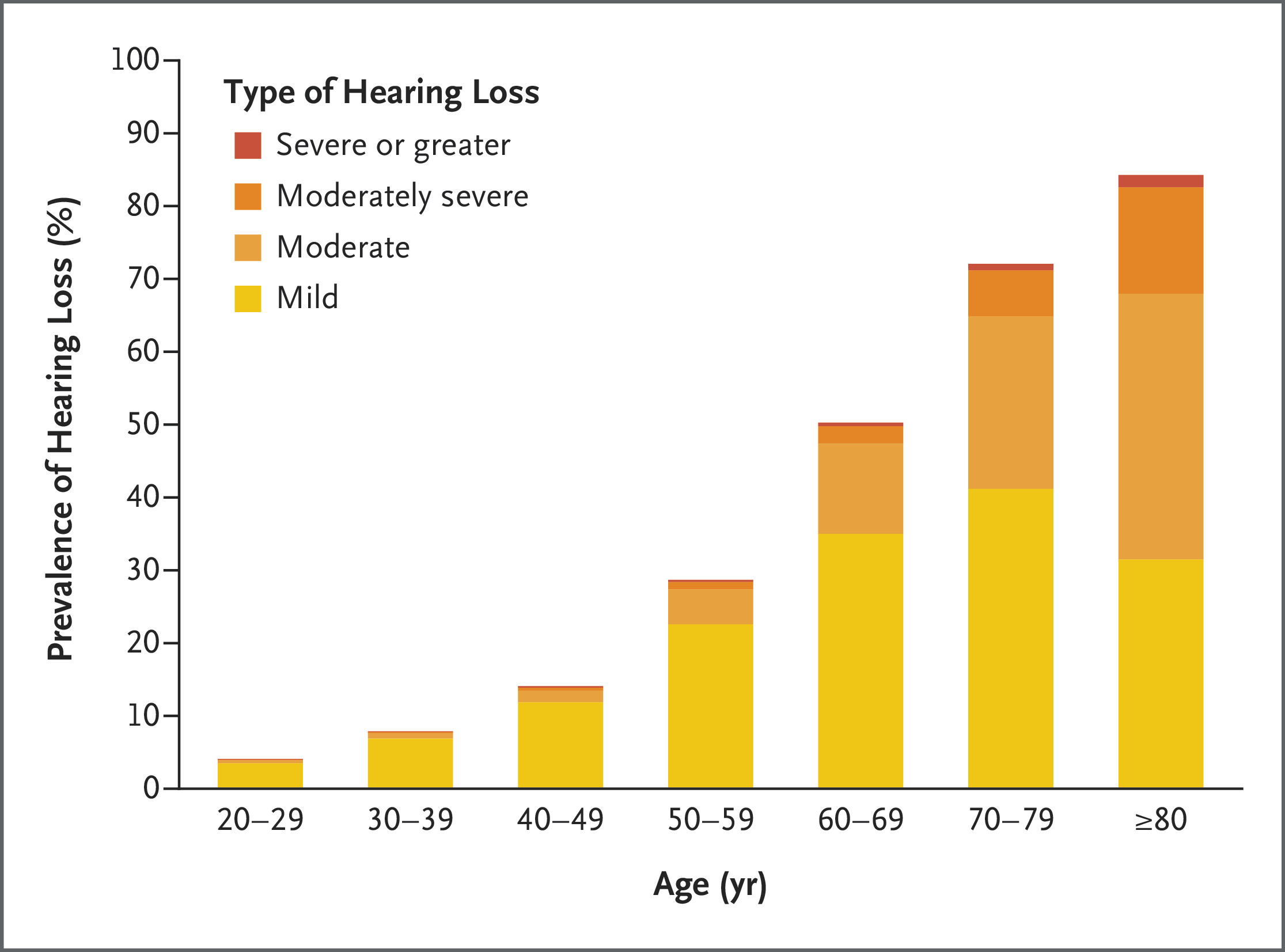
July 2024: Age-Related Hearing Loss
Age‑related hearing loss is nearly universal and now affects more than two‑thirds of adults ≥ 60; beyond communication problems, it is the single largest potentially modifiable risk factor for dementia later in life.
June 2024: Isatuximab, Bortezomib, Lenalidomide, and Dexamethasone for Multiple Myeloma
Adding the anti‑CD38 antibody isatuximab to the standard bortezomib + lenalidomide + dexamethasone (VRd) regimen kept newly diagnosed, transplant‑ineligible multiple‑myeloma patients in remission far longer than VRd alone. After five years, 63 % of people on the four‑drug combination were still free of disease progression versus 45 % on VRd (hazard ratio 0.60).
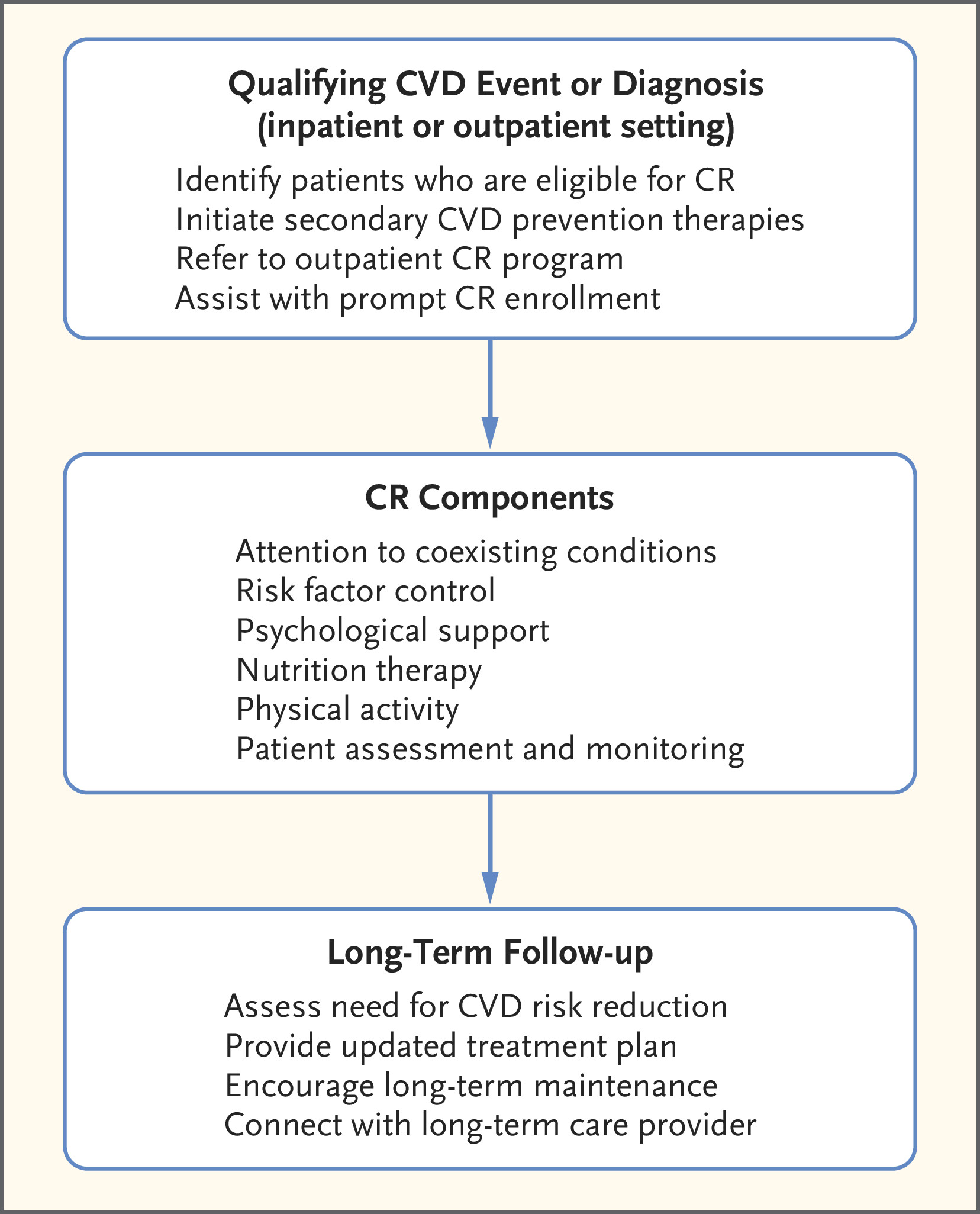
May 2024: Cardiac Rehabilitation — Challenges and Advances
Cardiac‑rehabilitation programs are lifesaving, but wide gaps in how exercise is prescribed and progressed mean many older adults miss out on the full benefit.